Shipping Analytics: how to analyse delivery metrics and why you should
With shipment analysis, you can monitor delivery performance, analyse actual costs, identify inefficiencies and improve the customer experience.
2. Enter the costs for the period and the total number of orders.
What's Shipping Analytics
Discover the basics of analysing shipments and returns.
Benefits of shipment analysis
Why should you analyse your shipments? Find out here.
Shipping KPIs and key metrics
Transit time, return rate, delivery time... these are the shipping KPIs..
Business intelligence
How to implement a shipment analysis system? Let's start with the basics.
Resources
Statistics, case studies and trends in shipping analytics to stay up to date.
FAQs
Everything you wanted to know about shipment and return analysis.

Shipping analytics is the process of collecting, organising and analysing shipping-related data (transit times, costs, returns, carrier performance, volumes, etc.) to gain insights that support operational and strategic improvement.
This approach makes it possible to turn raw, fragmented data into structured information that can be used to measure efficiency, anticipate issues, optimise costs and improve the customer experience.

Cost control: shipping costs often represent a significant share of an ecommerce business’s total logistics costs.
Visibility and transparency: enables a unified view of all shipping data, including costs, delivery times and carrier performance.
Data-driven decision-making: allows operational and strategic decisions to be made based on real business data and statistics.
Process optimisation: analysing shipments helps identify inefficiencies, reduce lead times, minimise errors and returns, and improve overall service quality.
Improved customer experience: faster and more reliable deliveries increase customer satisfaction and trust, supporting long-term loyalty.
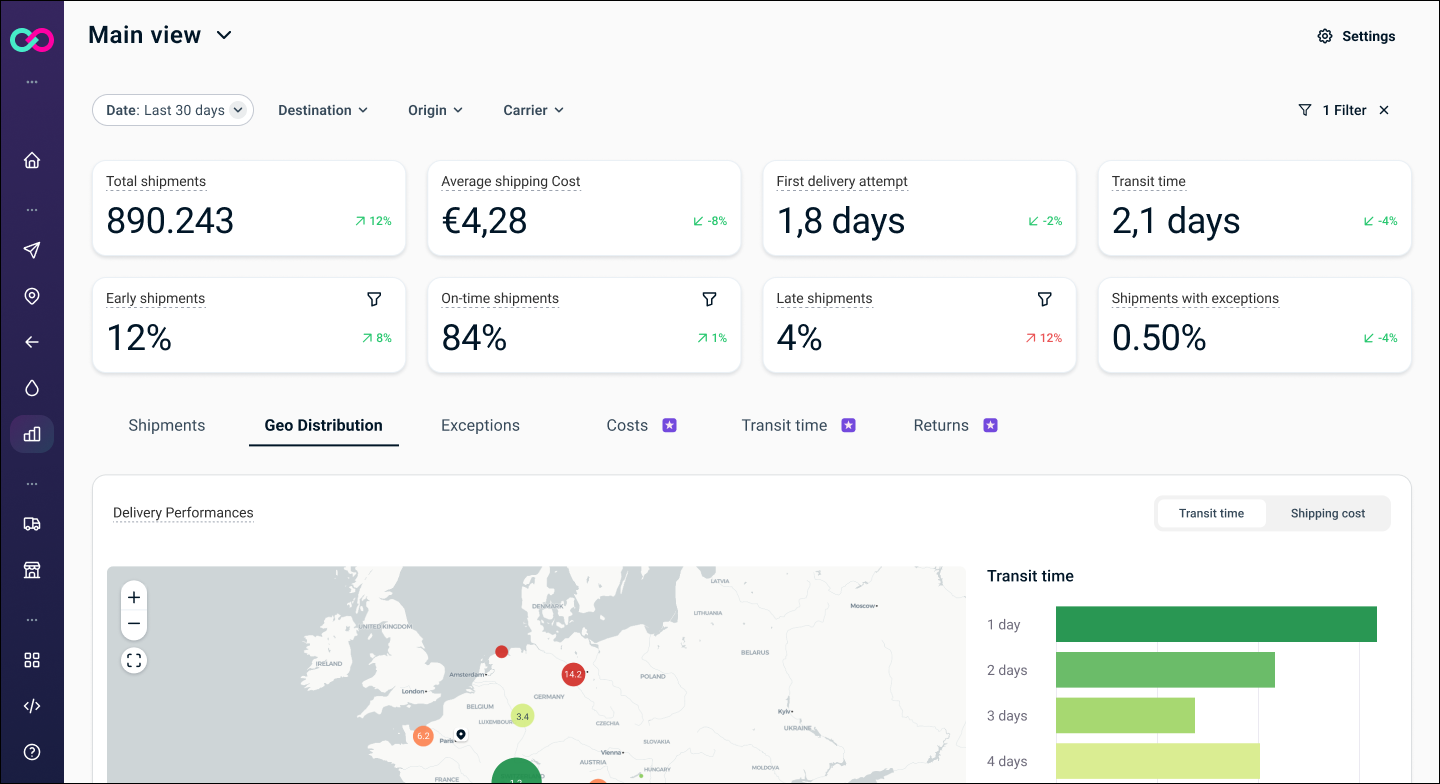
- Average delivery time / transit time: measures how long parcels take to reach their destination.
- On-time delivery rate: the percentage of shipments delivered within the promised timeframe.
- Average cost per shipment / per order: useful for understanding the impact of logistics costs on revenue.
- Return rate: helps assess the reliability and quality of deliveries.
- Carrier performance, such as error rates, failed deliveries and damaged shipments.
- Hidden costs and surcharges, for example extra carrier fees, delays, returns to sender, returns handling, and related charges.

Implementing a shipping analytics system first and foremost means bringing order to data: delivery times, costs, carrier performance and returns.
Once this information has been collected and consolidated, it becomes much easier to understand how shipments are really performing.
Clear, up-to-date dashboards make it possible to quickly identify delays, inefficiencies or meaningful trends, turning what was once based on intuition into something measurable. This is where more informed decisions take shape, helping optimise costs, improve service quality and make deliveries more seamless.